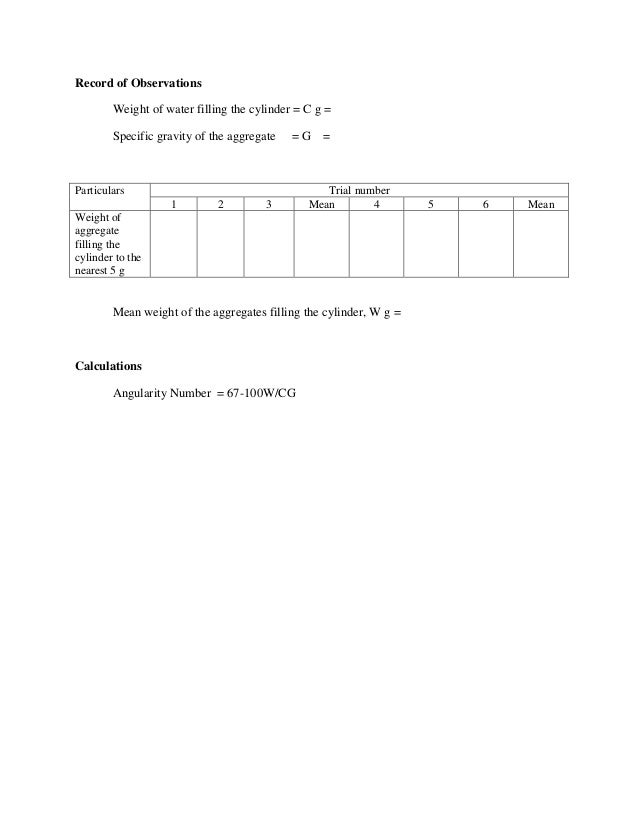
Angularity test 124236-Angularity number test nptel
Fine Aggregate Angularity Plastic Limit Surface Moisture Tests CHAPTER FIVE AGGREGATE SPECIFICATIONS AND REQUIREMENTS Physical Quality Requirements Fine Aggregates accurate to 02 g or 01% of the test load, whichever is greater, throughout the range of use 2) Laboratory oven capable of maintaining a temperature of 230 ± 9 °F,The void content of compacted aggregate is largely dependent upon the roundness (or angularity) of the component particles so that the percentage of voids in a standardised test can be used as a quantitative measure of particle angularity 114 A singlesized, wellrounded beach gravel produces a void content of 33% and this has been established as the zero baseline for the 'angularity number', which is represented by the percentage of voids in excess of 33% (ie angularity numberProcedure of Angularity Number Test for Coarse Aggregate Sieve the aggregate sample with sieves specified in Table 1 Fill the metal cylinder with water and record its volume Take sufficient quantity of aggregate to perform the test Compact the aggregate in three layers, each layer being given

Fine Aggregate Angularity Test Apparatus Hardyniec 05 Download Scientific Diagram
Angularity number test nptel
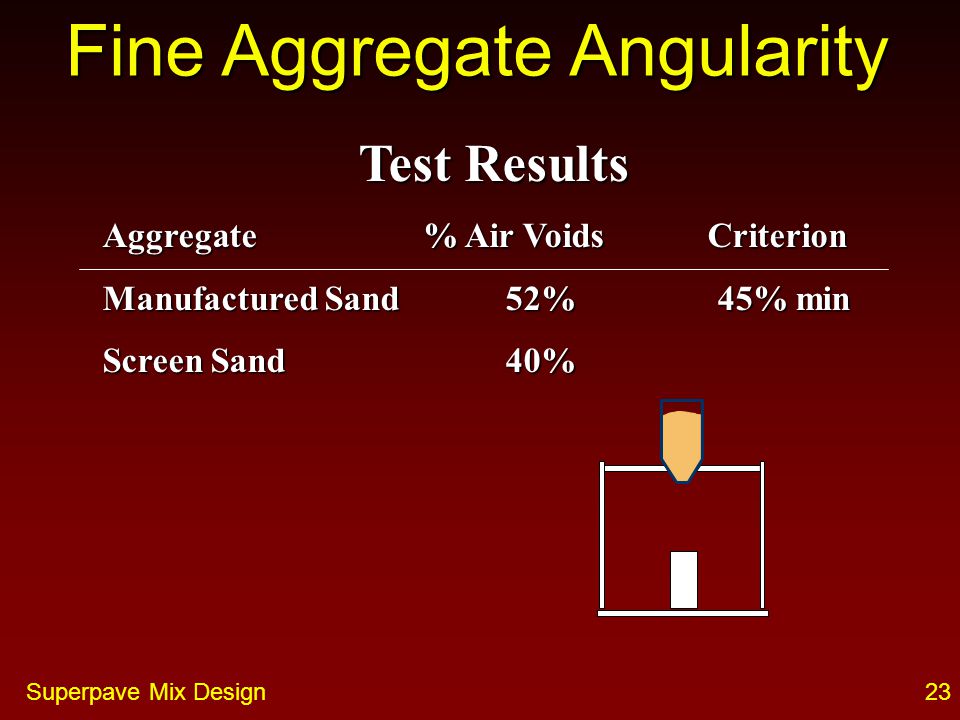
Angularity number test nptel-The uncompacted voids test is an indirect measure of aggregate shape, angularity, and texture, and works under the assumption that particles that are more flat and elongated, are more angular, have more texture, or are a combination thereof, will not pack as tightly and therefore will have a higher uncompacted void contentThe Fine Aggregate Angularity test (FAA), adopted by Superpave to evaluate and quantify the shape, angularity and surface texture of fine aggregate particles, has lead a lot of doubts regarding its suitability


I Cycle
Shape, angularity, and surface texture on the engineering properties can also be inferred Petrological methods The shape of the aggregate can be described by its length, width, thickness, sphericity, roundness, and angularity The surface texture is difficult to quantify and several visual charts and some sophisticated test methods have beenThis method of test determines the loose uncompacted void content of fine aggregate samples Uncompacted void content provides an indication of angularity, sphericity, and surface texture for an aggregate of known gradation B Reference Documents 1 DOTD S 101 Sampling Aggregates / Aggregate MixturesQUANTIFY SHAPE, ANGULARITY AND SURFACE TEXTURE OF AGGREGATES USING IMAGE ANALYSIS AND STUDY THEIR EFFECT ON PERFORMANCE by Dallas Little Senior Research Fellow
Angularity test helps define the nature of the fine aggregate For high volume roads Superpave recommends FAA's of 45 Brown and Cross indicated FAA's in the 42 to 45 range performed best in rut resistance The SHRP researchers took a conservative approach and set 45 as a minimum value for the FAA test for high volume roadsPROCEDURE (METHOD A) Obtain an aggregate sample by separating individual sizes from the No 8 (236 mm) sieve to the No 100 (150 mm) sieve Thoroughly mix the individual sieve increments with a spatula until it appears to be a homogeneous 190gram sample Position the jar and funnel section in theFine Aggregate Angularity Overview The fine aggregate angularity (FAA) test (Figure 1) is an indirect method of assessing the angularity of fine Background The FAA test indirectly measures the angularity of fine aggregate using the aggregate's uncompacted void Test Description The following
The performance of dense asphalt mixtures is influenced mainly by fine aggregate characteristics, such as shape, angularity and surface texture The Fine Aggregate Angularity test (FAA), adopted byBuy AS Methods for sampling and testing aggregates Angularity number from SAI GlobalAngularity in general is the absence of rounding of particles of an aggregate This test is performed to determine the angularity number ie the absence of roundedness or the degree of angularity of the aggregate specimen RELATEDTHEORY SHAPES OF PARTICLES The usual shapes of the particles are;



Fine Aggregate Angularity Pavement Interactive


Superpave Mix Design Superpave Mix Design Ppt Video Online Download
Objective For determination of angularity number of coarse aggregates Reference Standards IS 2386 (Part I) – 1963 – Method of test for aggregates for concrete (Part I) Particle size and shape Equipment & Apparatus Balance (010kg) Sieves (,16,125,10,63,475mm) Metal cylinder Tamping rod Scoop Test Sample Preparation The test sample consist of aggregate retained between theThe ASTM C1252 angularity test, and the threedimensional digital and scanning electron microscope visual analysis using ASTM D24 angularity When these tests were completed, the ASTM A1081 standard test method for evaluating the bond of sevenwire steel prestressing including the ASTM C109 mortar cube test was performedThe Fine Aggregate Angularity Apparatus determines the uncompacted void content of fine aggregates to determine angularity and sphericity properties that affect the workability of mixed designs Gilson offers two models for this popular test Each sample is mixed with a spatula until homogeneous and transferred to the hopper while the discharge opening is blocked with a finger


Shape Analysis Of Railway Ballast Stones Curvature Based Calculation Of Particle Angularity Scientific Reports



Fine Aggregate Angularity Test Apparatus Hardyniec 05 Download Scientific Diagram
This is an indirect method for estimating fine aggregate angularity and texture The FAA test is based on the assumption that more fractured faces will result in higher void content in the loosely compacted sample;The procedure specified by ASTM A1081 uses only fine aggregate in the mixture proportions Sand angularity is a variable of interest because it could affect strand acceptance and the reliability of the ASTM A1081 strand bond test Four sands were tested, each of which was subjected to a full ASTM A1081–style testThe ASTM C1252 angularity test, and the threedimensional digital and scanning electron microscope visual analysis using ASTM D24 angularity When these tests were completed, the ASTM A1081 standard test method for evaluating the bond of sevenwire steel prestressing including the ASTM C109 mortar cube test was performed



Angularity Number Test Results Download Scientific Diagram



Solved Given The Following Information Determined Using T Chegg Com
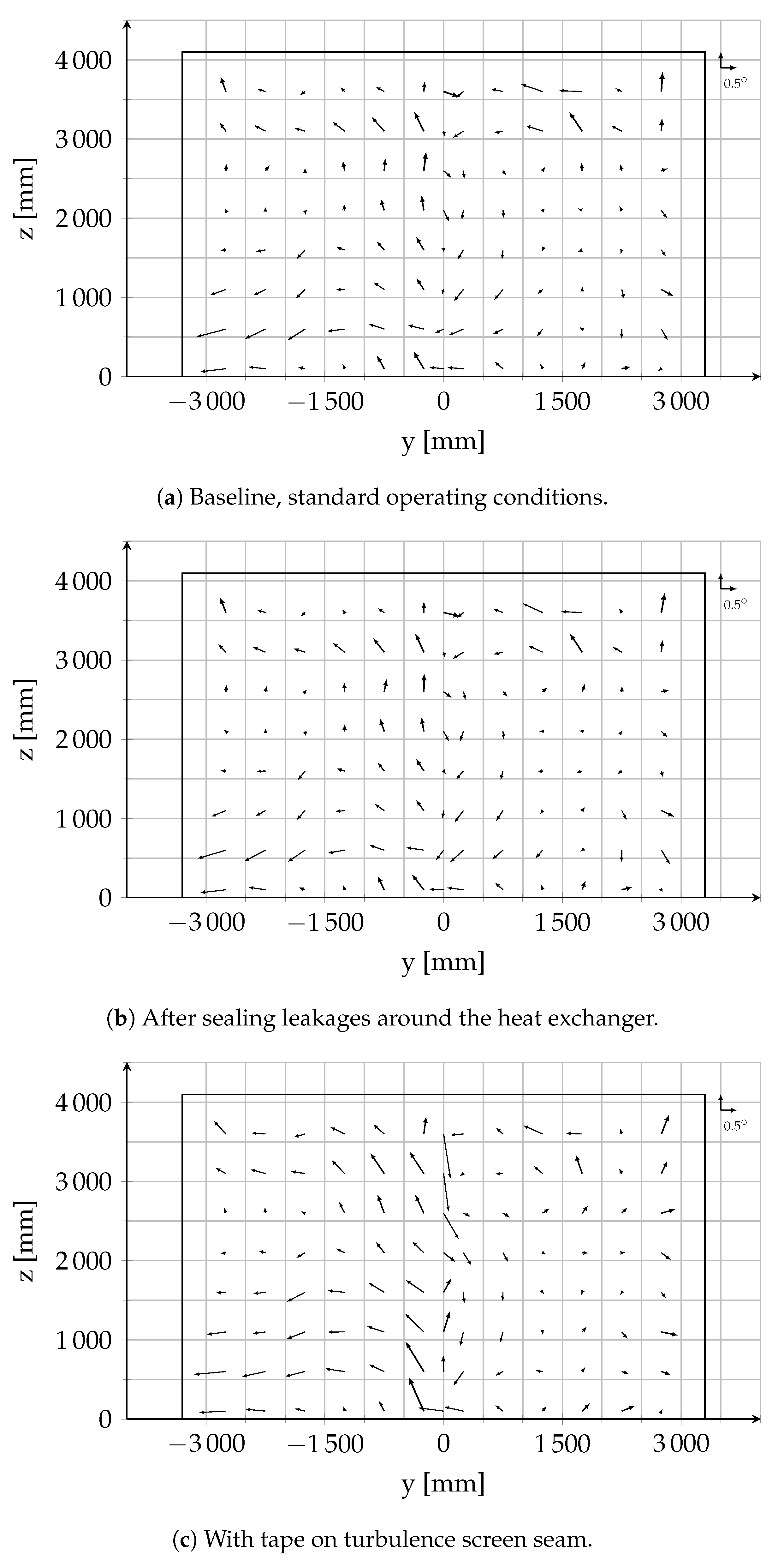
FA = flow angularity, degrees M∞ = test section Mach number NTF = National Transonic Facility PFI = Pathfinder I model pT ∞ = test section total pressure, psia q0 = dynamic pressure cutoff for transition from Eq (3) to Eq (4) q∞ = test section dynamic pressure, psf R = range, degrees Rfit = fit to the means of the subgroup ranges, degreesFor the fine aggregate angularity measurement, the current Superpave testing method, AASHTO T304, is considered reasonable in a practical sense Rutting performance test results indicate that higher angularity in the mixture improves rut resistance due to better aggregate interlockingThis test method provides objective and direct measurements of aggregate volume, shape (ï¬ atness and elongation), angularity, and texture to quantify these properties and provide repeatable results that are compar atively more beneï¬ cial for use in performance prediction of highway pavements and structures


Angularity Testing Meter China Angularity Testing Meter Supplier Manufacturer Shenxian Instruments



Angularity Number Angularity Number Aim To Determine The Angularity Number Of A Given Coarse Aggregate Sample Supplied To You Practical Course Hero
Systems are presented for capturing angularity and texture images and are analyzed with the help of the aggregate imaging system (AIMS) The goal is to measure surface properties of both coarse and fine aggregates and relate these properties to performanceUncompacted Void Content of Fine Aggregate (Fine Aggregate Angularity Test) AASHTO Designation T 304 161 Scope The fine aggregate angularity test determines the loose uncompacted void content of a fine aggregate material The void content information derived from this test gives you an indication of the effectNCDOT Material and Tests Unit, for their cooperation and providing test data for this research study Finally, the authors would like to thank the members and visiting scholars of texture and angularity properties and the permanent deformation behavior


Energies Free Full Text Flow Angularity Investigations In An Automotive Slotted Wall Wind Tunnel Html



A Flat And Elongated Test Setup B Fine Aggregate Angularity Setup Download Scientific Diagram
Angularity in general is the absence of rounding of particles of an aggregate This test is performed to determine the angularity number ie the absence of roundedness or the degree of angularity of the aggregate specimenThe 19 different gradation and aggregate source combinations are tested using the Fine Aggregate Angularity Test Method C as outlined by AASHTO T304 (03) and ASTM C1252 (03), the direct shearThis method of test determines the loose uncompacted void content of fine aggregate samples Uncompacted void content provides an indication of angularity, sphericity, and surface texture for an aggregate of known gradation B Reference Documents 1 DOTD S 101 Sampling Aggregates / Aggregate Mixtures


Fine Aggregate Angularity Pavement Interactive



2 11 Fine Aggregate Angularity Test Set Up Download Scientific Diagram
11 These test methods cover the determination of the loose, uncompacted void content of a sample of fine aggregate When measured on any aggregate of a known grading, void content provides an indication of that aggregate's angularity, sphericity, and surface texture compared with other fine aggregates tested in the same gradingAggregate angularity of individual particles is defined by WipShape, a digital imagebased system, as the Minimum Average Curve Radius Physical tests including Uncompacted Void Content, Index of Particle Shape and Texture (Compacted Voids), and Percentage of Fractured Particles, were conducted usingIn angularity number test, a quantity of single sized aggregate is filled into metal cylinder of 3 liter capacity Then the aggregate is compacted in a standard manner and the percentage of void found out To know the detail procedure click here If the void content of the aggregate is 33% the angularity of such aggregate is considered 0



Fine Aggregate Angularity Test Youtube



China Fine Aggregate Angularity Test Apparatus China Angularity Apparatus Fine Aggregate Angularity Tester
This Lecture includes following Topics Types of Shape TestWhat is Flakiness Index, Elongation Index & Angularity Index?Why it is done?Apparatus required toMethod of Test for Fine Aggregate Angularity 1 Scope The fine aggregate angularity test determines the loose uncompacted void content of a fine aggregate sample 2 Apparatus 21 Cylinder dimensions Capacity of approximately 338 oz, inside diameter 15 in, inside height 34 in, and base shall be 024 in thick and securely sealedThe National Aggregate Association (NAA) has developed a test to objectively quantify the angularity of fine aggregates The NAA test was used to develop the draft AASHTO TP3 entitled "Standard Test Method for Uncompacted Void Content of Fine Aggregate (As Influenced by Particle Shape, Surface Texture, and Grading)"·



Exp 2 Aggregate Angularity Number Civil Engineers Pk
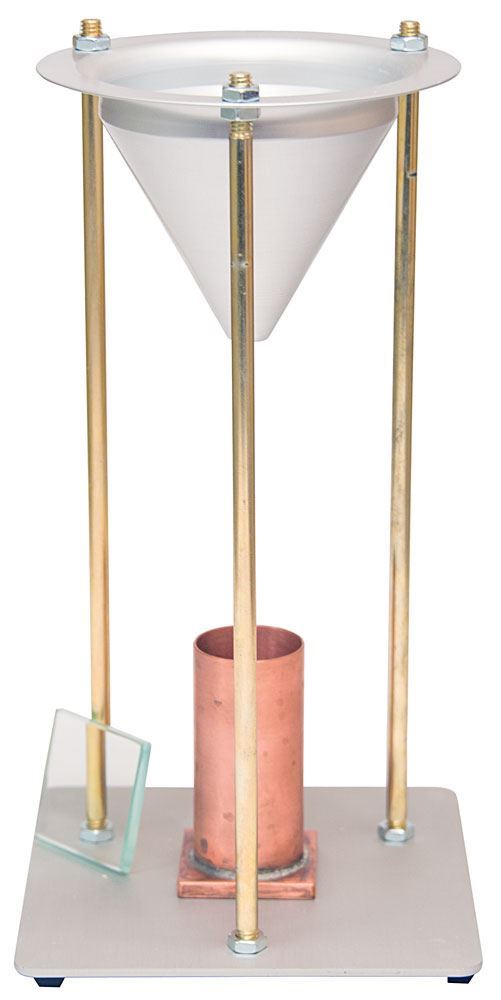



Fine Aggregate Angularity Apparatus Gilson Co
C54 Transportation Engineering Lab ExperimentThe aggregate angularity test consists of filling the upper cylindrical hopper with the aggregate and then opening the gate at the bottom of the hopper Fig 6(a) presents the apparatus used for the coarse aggregate angularity test, and Fig 6(b)–(d) present the 19, 13, and 10 mm aggregates remaining in the container, respectively In thisThis test is performed to determine the angularity number ie the absence of roundness or the degree of angularity of the aggregate specimen The degree of packing of particles of single sized aggregate depends upon the angularity of aggregate The angularity of the aggregate can be estimated from the properties of voids in a sample of



Exp 2 Aggregate Angularity Number Civil Engineers Pk



Correlate Aggregate Angularity Characteristics To The Skid Resistance Of Asphalt Pavement Based On Image Analysis Technology Sciencedirect
Buy AS Methods for sampling and testing aggregates Angularity number from SAI GlobalTo determine the angularity of the aggregate the coarse aggregate angularity test is performed Coarse aggregate angularity is defined as the percent by weight of aggregates larger than 475 millimeters with one or more fractured faces Many State Highway Agencies have protocols to measure coarse aggregate angularityRounded (river gravel) Flaky (laminated rock



Aggregate Angularity Apparatus Parsros Malzeme Test Cihazlari



Aggregate Properties Hma Ppt Video Online Download
Angularity is measured by constraining a part, usually with a sine bar, tilted to the reference angle, so that the reference surface is now parallel to the granite slab By setting the part at an angle the flatness can now be measured across the now horizontal reference surface The entire variation must not fall outside the tolerance zoneUnder NCHRP Project 430A, â Test Methods for Characterizing Aggregate Shape, Tex ture, and Angularity,â Texas A&M University of College Station was assigned the objective of identifying or developingâ for use in central and field laboratoriesâ suitable test methods for measuring shape, texture, and angularity characteristics of aggregates used in HMA, hydraulic cement concrete, and unbound base and subbase layers of highway pavementsThis second generation Aggregate Image Measuring System provides objective shape, angularity, and surface texture information for aggregate using computer, camera, lighting, and microscope technology The system was designed to eliminate subjectivity by removing the human influence and improve productivity and precision through computer analysis


Test Methods For Characterizing Aggregate Shape Texture And Angularity The National Academies Press



Angularity Number Test For Coarse Aggregate Shape Test For Aggregate
Method of Test for Fine Aggregate Angularity 1 Scope The fine aggregate angularity test determines the loose uncompacted void content of a fine aggregate sample 2 Apparatus 21 Cylinder dimensions Capacity of approximately 338 oz, inside diameter 15 in, inside height 34 in, and base shall be 024 in thick and securely sealedThe Fine Aggregate Angularity test (FAA), adopted by Superpave to evaluate the shape, angularity and surface texture of fine aggregate particles, has left a lot of doubts regarding its suitability The objective of this work is to verify if the FAA test is really able to classify fine aggregates and identify the good ones to be used in asphalt mixturesCoarse Aggregate Angularity Overview The coarse aggregate angularity (CAA) test is a method of determining the angularity of coarse aggregate Background The CAA test determines by visual inspection the amount (as a percent by weight) of coarse aggregate Test Description The following is a



Angularity Number Test For Coarse Aggregate Shape Test For Aggregate
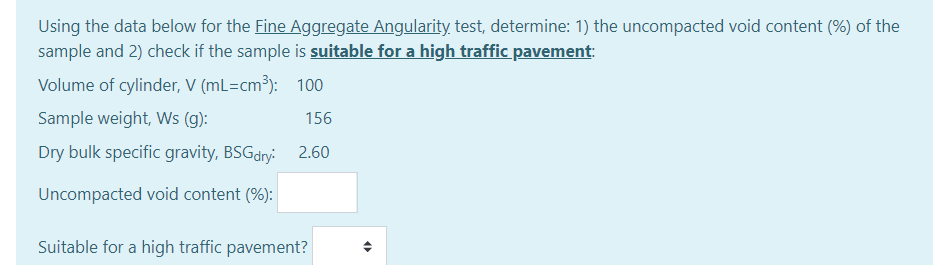


Solved Using The Data Below For The Fine Aggregate Angula Chegg Com
Angularity definition 1 the quality of having angles rather than curves 2 the quality of having or seeming to have Learn more11 These test methods cover the determination of the loose, uncompacted void content of a sample of fine aggregate When measured on any aggregate of a known grading, void content provides an indication of that aggregate's angularity, sphericity, and surface texture compared with other fine aggregates tested in the same gradingThis test is performed to determine the angularity number ie the absence of roundness or the degree of angularity of the aggregate specimen The degree of packing of particles of single sized aggregate depends upon the angularity of aggregate The angularity of the aggregate can be estimated from the properties of voids in a sample of aggregate compacted in a specified manner The angularity number ranges from zero, for a highly rounded gravel to about 11 for freshly crushed angular



Angularity Number Test For Coarse Aggregate Shape Test For Aggregate


Buy Aggregate Angularity Apparatus Manufacturers And Suppliers Factory Price Serve Real
Shape, angularity, and surface texture on the engineering properties can also be inferred Petrological methods The shape of the aggregate can be described by its length, width, thickness, sphericity, roundness, and angularity The surface texture is difficult to quantify and several visual charts and some sophisticated test methods have beenAngularity test helps define the nature of the fine aggregate For high volume roads Superpave recommends FAA's of 45 Brown and Cross indicated FAA's in the 42 to 45 range performed best in rut resistance The SHRP researchers took a conservative approach and set 45 as a minimum value for the FAA test for high volume roadsHowever, this is not always true The paving and aggregate industries have found that cubical shaped particles, even with 100



Appendixes To Nchrp Report 555 Test Methods For Characterizing Aggregate Shape Texture And Angularity Appendixes To Nchrp Report 555 Test Methods For Characterizing Aggregate Shape Texture And Angularity The National Academies Press



Influence Of Coarse Aggregate Angularity On Asphalt Mixture Macroperformance Skid Resistance High Temperature And Compaction Performance Journal Of Materials In Civil Engineering Vol 32 No 5
The SG42 Coarse Aggregate Angularity Apparatus measures uncompacted void content of coarse aggregateThe testing apparatus is recommended to evaluate aggregates for HotMix Asphalt (HMA) pavement Gradation and void content data provide an indication of angularity, sphericity, and surface texture that can be related to permanent deformation and fatigue cracking of asphalt



Angularity Number Road Surface Concrete



I Cycle



Angularity Number Road Surface Concrete


Testing Machine For The Construction Industrial Zhuozhou Tianpeng Imp And Exp Trade Ltd Materials Testing Equipment



Uncompacted Voids Test For Measuring Void Ratio Coarse Aggregate Download Scientific Diagram



Coarse Aggregate Angularity Apparatus Classification Devices For Aggregate Testing And Aggregate Testing Equipment Certified Material Testing Products



Laboratory Ii Aggregate Testing October 6 And 7 Rowan



Fine Aggregate Angularity Faa Test Equipment Download Scientific Diagram


Quantification Of Coarse Aggregate Angularity By A Newly Developed Auto Grader Machine



5 Fine Aggregate Angularity Recommendations Download Table



Solved Given The Following Information Determine Using Th Chegg Com



Chapter 2 Findings Test Methods For Characterizing Aggregate Shape Texture And Angularity The National Academies Press



Fine Aggregate Angularity Test Excel Template Excel Xlsx Free Download Pikbest


Fine Aggregate Angularity Apparatus Download Scientific Diagram



Lec 28 Civil Engineering By Piyush Sir Building Material Construction Test On Aggregate Ese Youtube


Quantification Of Coarse Aggregate Angularity By A Newly Developed Auto Grader Machine



Influence Of Coarse Aggregate Angularity On Asphalt Mixture Macroperformance Skid Resistance High Temperature And Compaction Performance Journal Of Materials In Civil Engineering Vol 32 No 5



Angularity Test Apparatus Lab Testing Instruments प रय गश ल म पर क षण क उपकरण In Transport Nagar Pune Hitech Engineering Testing Technology Id



Fine Aggregate Angularity Pavement Interactive



What Is Angularity Number Of Aggregate Civilblog Org



Determination Of The Angularity Number Of The Given Aggregate Sample Construction Aggregate Road Surface



Recycled Aggregate Of Recycled Aggregate Association Which Lack Angularity Recycled Aggregate Environmental Laboratory Test Number A S Type I And M Type Ii Coarse Aggregate



Fine Aggregate Angularity Test We Civil Engineers
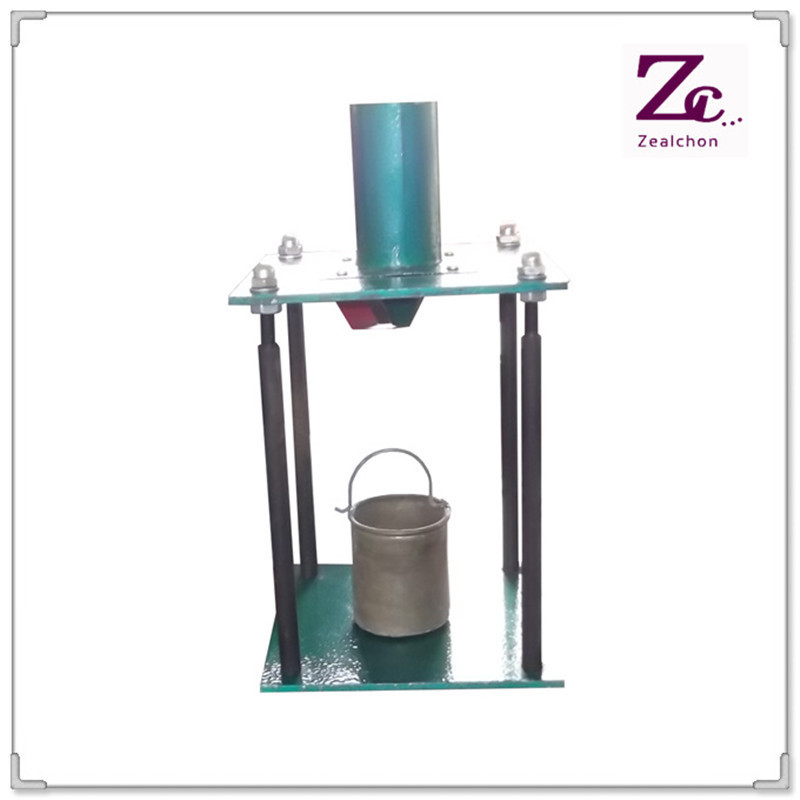



C071 Fine Aggregate Grain Angularity Tester Price Use For Aggregate Grain Angularity Test



China Void Content Apparatus For Coarse Aggregate China Coarse Aggragate Angularity Apparatus Coarse Aggregate Angularity



Angularity Number Of Ca Kilogram Construction Aggregate



Stxcj 1 Fine Aggregate Grain Angularity Testing Meter Buy Fine Aggregate Grain Angularity Testing Meter Aggregate Impact Test Apparatus Soil Aggregate Testing Product On Alibaba Com



Front Matter Test Methods For Characterizing Aggregate Shape Texture And Angularity The National Academies Press



Fine Aggregate Angularity Apparatus Classification Devices For Aggregate Testing And Aggregate Testing Equipment Certified Material Testing Products



Angularity Number Test For Coarse Aggregate Shape Test For Aggregate



The Effect Of Fine Aggregate Angularity Asphalt Content And Performance Graded Asphalts On Hot Mix Asphalt Performance Semantic Scholar



Angularity Apparatus



Coarse Aggregate Angularity Apparatus Gilson Co


Fine Aggregate Angularity Pavement Interactive



Solved Given The Following Information Determined Using T Chegg Com



Determination Of Angularity Number Of The Given Aggregate Sample Seismic Consolidation


Coarse Aggregate Angularity Pavement Interactive



Appendix D Test Methods For Measuring Aggregate Characteristics Appendixes To Nchrp Report 555 Test Methods For Characterizing Aggregate Shape Texture And Angularity The National Academies Press


Coarse Aggregate Angularity Pavement Interactive



Coarse Aggregate Angularity Pavement Interactive



Civil Engineering Study Material Problem And Solution Angularity Number Test Of Aggregate



Void Content Apparatus Fine Aggregate Angularity Hma Lab Supply


Quantification Of Coarse Aggregate Angularity By A Newly Developed Auto Grader Machine



Angularity An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



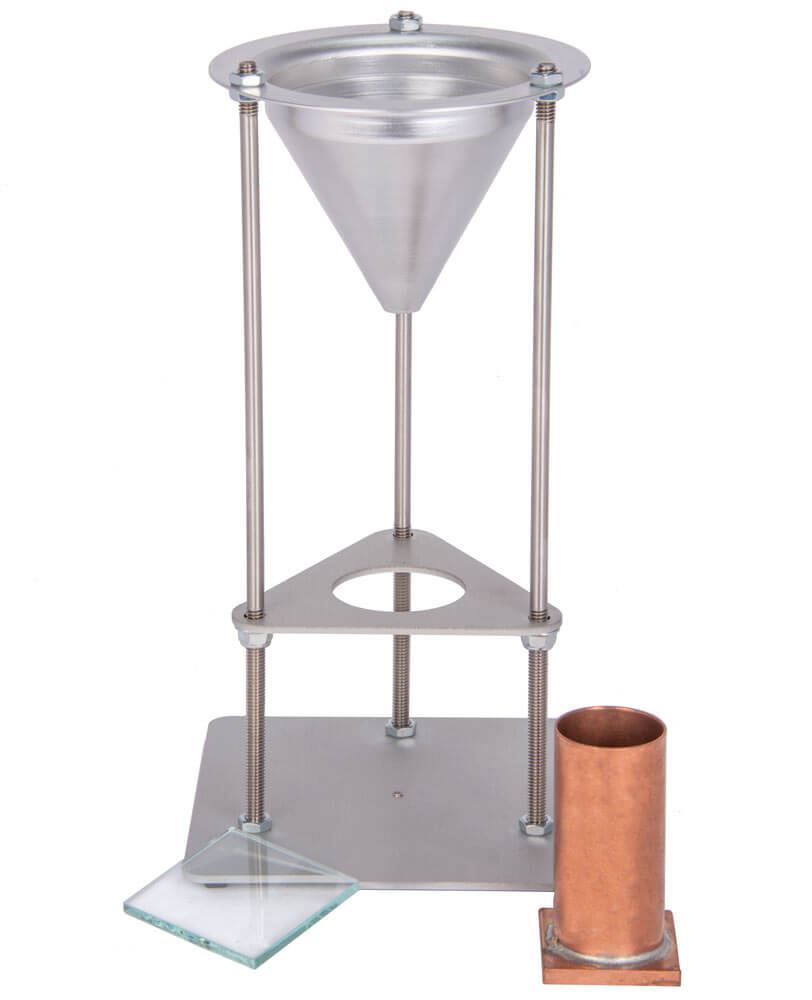
C071 Fine Aggregate Grain Angularity Tester Price Use For Aggregate Grain Angularity Test



Aggregate Angularity Apparatus Parsros Malzeme Test Cihazlari



Fine Aggregate Angularity Test Youtube



Develop Draft Chip Seal Cover Aggregate Specification Based On Aggregate Imaging System Aims Angularity Shape And Texture Test Results



Fine Aggregate Angularity Apparatus Gilson Co
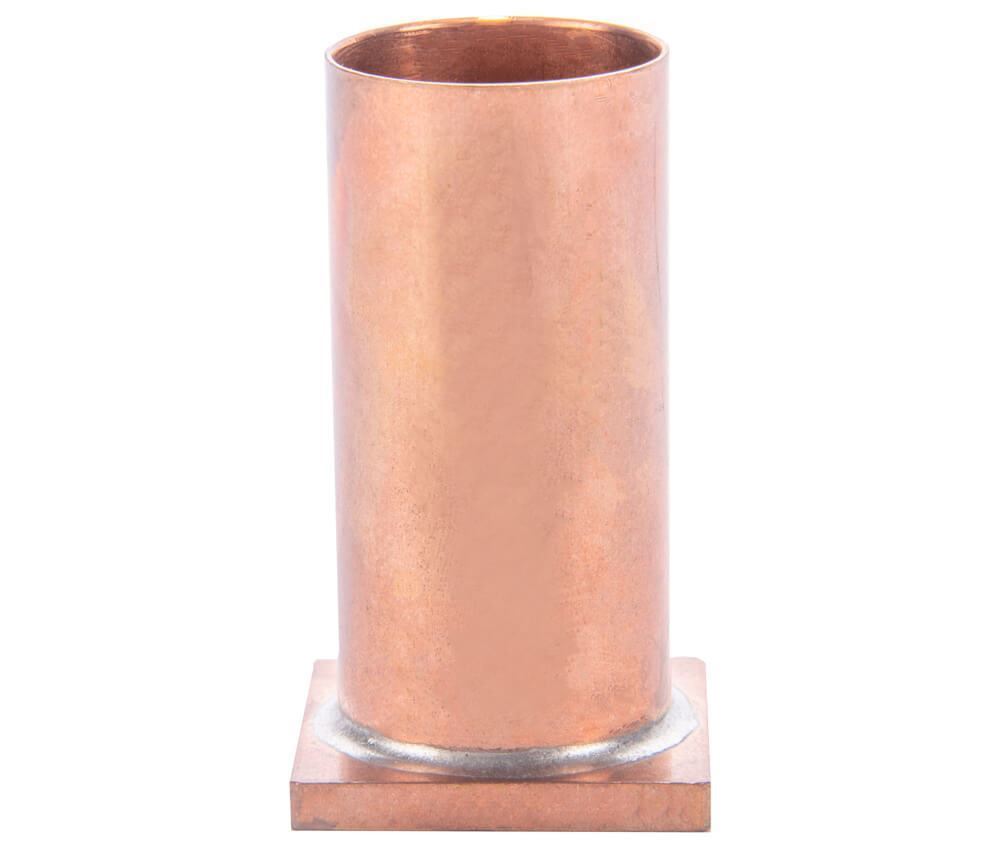



Fine Aggregate Angularity Apparatus Gilson Co



Fine Aggregate Angularity Test Excel Template Excel Xlsx Free Download Pikbest


Fine Aggregate Angularity Pavement Interactive



7c Vecat Coarse Aggregate Angularity Test Danny Poole 1 Youtube



Solved Using The Data Below For The Fine Aggregate Angula Chegg Com



Fine Aggregate Angularity Test Method A Youtube



Angularity An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Quantification Of Coarse Aggregate Angularity By A Newly Developed Auto Grader Machine



Chapter 4 Conclusions And Suggested Research Test Methods For Characterizing Aggregate Shape Texture And Angularity The National Academies Press


Fine Aggregate Angularity Test Apparatus
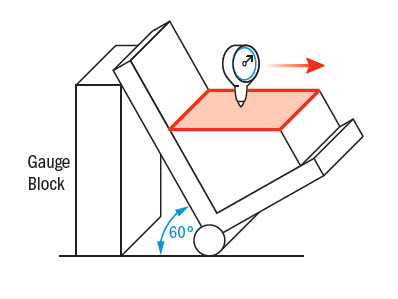


Angularity Gd T Basics



Solved Ed A Fine Aggregate Angularity Faa Test Was Cond Chegg Com



Pdf Determination Of The Angularity Number Of The Given Aggregate Sample Shaheer Ahmad Academia Edu
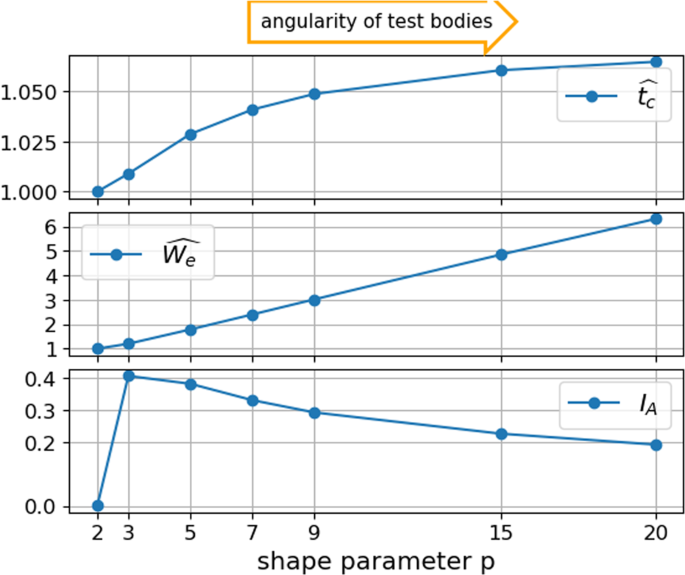


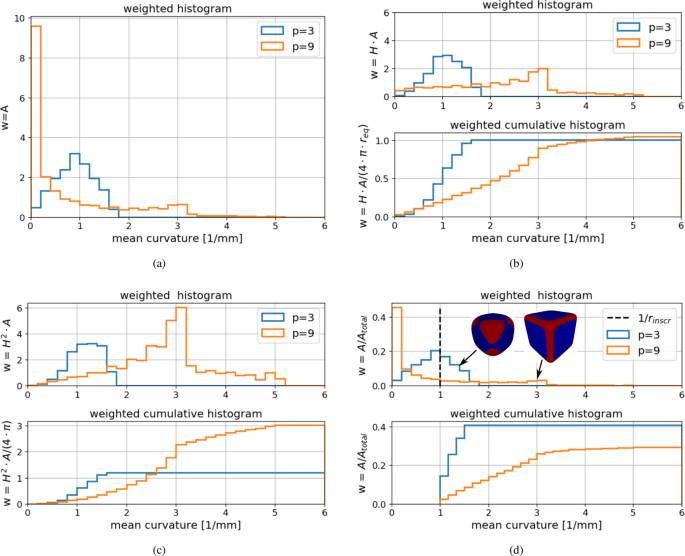
Shape Analysis Of Railway Ballast Stones Curvature Based Calculation Of Particle Angularity Scientific Reports



Aggregates Ppt Video Online Download


コメント
コメントを投稿